My iPhone is a pretty much constant presence in my life, from checking my email first thing in the morning to watching my nephews play with the DoodleBuddy app. But until last week, I never seriously considered its impact on the environment.
That changed when Apple published greenhouse gas emissions from its operations and products for the first time. The report, available at www.apple.com/environment, goes farther than other consumer tech companies have by accounting for product usage.
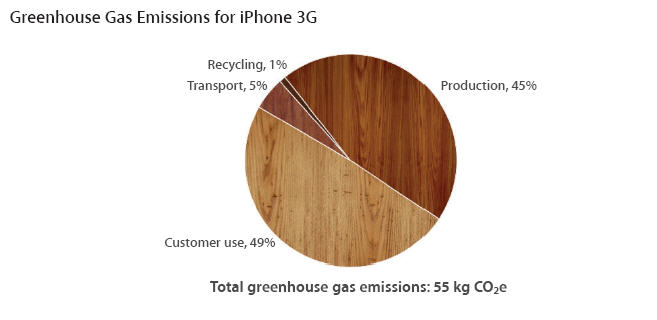
It turns out that my iPhone produces greenhouse gases equivalent to about 55kg of carbon dioxide over the full course of its lifecycle, from sourcing to recycling. My use of my iPhone produces about 27kg of carbon dioxide.
To put that in perspective, 55kg of CO2 is equivalent to burning 22 gallons of gasoline in a car or 8 propane cylinders on a backyard grill. If I planted 5 tree seedlings in my backyard tomorrow, it would take them 10 years to sequester the amount of carbon my iPhone produces.
OK, so what? Twenty-two gallons of gas and 10 trees ain’t such a bad trade given that the iPhone is… well… downright awesome.
Truly. The iPhone is one of the most successful consumer tech products in history. Apple has sold 21M iPhone units since Q3 2007, shattering sales records.
All those iPhones have produced a lot of carbon emissions, equivalent to 1.16b kg to be exact, or roughly the same amount as a coal-fired power plant in one year of operation.
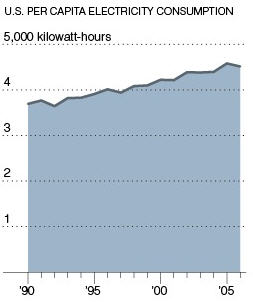
Source: New York Times
Bottom line: there isn’t enough land enough in the world to offset America’s greenhouse gas emissions from electronics by planting trees.
To halt our rising carbon emissions, America needs more than offsets. We need renewable energy alternatives at scale and stringent energy efficiency standards, especially for our electronics, “which now represent 15% of household power demand, and that is expected to triple over the next decade,” according to the New York Times and International Energy Agency.
Many are working hard to accomplish this goal. California recently proposed to ban the sale of high energy televisions. Flat-screen TVs and video game consoles can use more energy than refrigerators in some American homes today, due to a lack of mandatory efficiency standards. Massachusetts has followed suit by hearing testimony on TV efficiency.
Apple, in the same report cited above, announced that all of their desktop and laptop products now come with EnergyStar certification, an industry first. Going further, Apple also boldly withdrew from the US Chamber of Commerce, stating “Apple supports regulating greenhouse gas emissions, and it is frustrating to find the Chamber at odds with us in this effort.”
That’s a proactive step forward and a first for a major consumer brand. Other electronics manufacturers should follow Apple’s leadership.
Alex Patriquin is Founder and CEO of Digital Verdure, a digital media and sustainability company based in Cambridge, MA. Read more at his blog, DigitalVerdure.com.
